Enhancing photosynthetic CO2 fixation by assembling metal-organic frameworks on Chlorella pyrenoidosa
Dingyi Li, Hong Dong, Xupeng Cao, Wangyin Wang*, and Can Li*
Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 5337.
The CO2 concentration at ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) is crucial to improve photosynthetic efficiency for biomass yield. However, how to concentrate and transport atmospheric CO2 towards the Rubisco carboxylation is a big challenge. Herein, we report the self-assembly of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) on the surface of the green alga Chlorella pyrenoidosa that can greatly enhance the photosynthetic carbon fixation. The chemical CO2 concentrating approach improves the apparent photo conversion efficiency to about 1.9 folds, which is up to 9.8% in ambient air from an intrinsic 5.1%. We find that the efficient carbon fixation lies in the conversion of the captured CO2 to the transportable HCO3− species at bio-organic interface. This work demonstrates a chemical approach of concentrating atmospheric CO2 for enhancing biomass yield of photosynthesis.
近日,我组在提高微藻光合作用固碳方面取得新进展,发现利用金属有机框架材料(MOFs)直接空气捕集二氧化碳(CO2)与生物碳浓缩耦合机制,强化了环境到细胞的CO2传质,微藻光合作用固碳效率由5.1%提高至9.8%。
在自然光合作用中,植物利用太阳光、水、CO2合成生物质。但是,植物的光合作用效率主要受到光照质量和CO2捕集与传输方面因素的限制,制约了光合作用合成生物质的效率。针对这些科学问题,我组前期通过添加胞外人工电子梭,提高了光吸收饱和点,解除了光抑制(Natural. Sciences.,2021);在光合细胞内引入纳米金,研究了暗反应固碳酶催化的限制因素(ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng.,2023)。目前,在大气水平CO2浓度下,如何捕集浓缩CO2并高效传输到Rubisco酶提高固碳反应动力学,仍是植物光合作用研究领域的挑战课题。
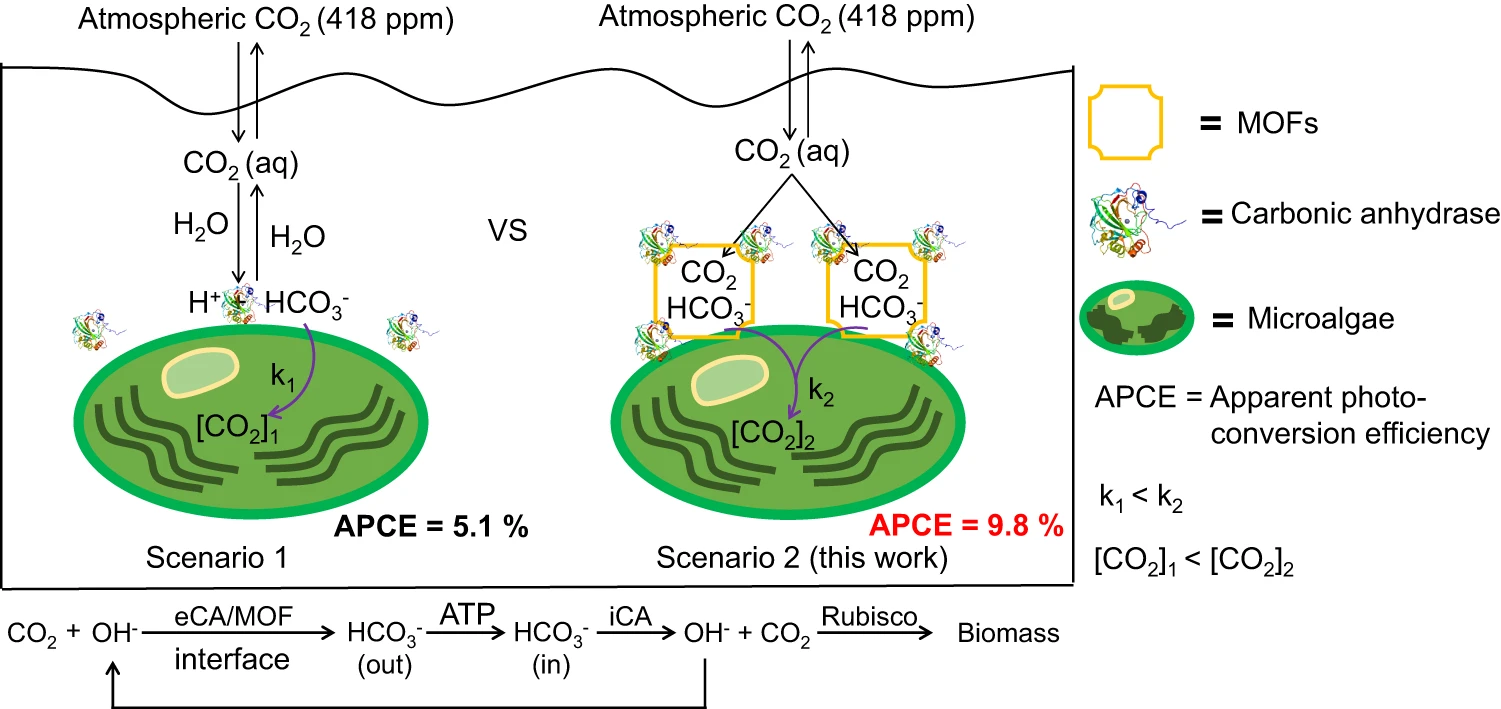
本工作中,我组提出了化学与生物杂合的策略,在光合微藻表面自组装多孔材料MOFs,实现CO2的直接空气捕集与生物转化。研究发现,MOF材料通过静电作用在小球藻表面自组装,将空气中的CO2捕获并富集在微藻细胞,使微藻光合放氧速率对CO2的亲和力提高了82%。团队通过酶动力学实验发现,小球藻分泌的胞外碳酸酐酶可将MOFs捕集的CO2水合为碳酸氢根,生物膜上的转运蛋白将碳酸氢根运输到叶绿体中的蛋白核内,从而提升了小球藻Rubisco酶周围的CO2浓度。该效应诱导固碳关键酶Rubisco的表达量提高,加快小球藻光合固碳速率。MOFs捕集CO2的功能使得微藻细胞在强化暗反应的同时,也缓解了光反应在光胁迫下遭受的抑制。光能到生物质的表观转化效率从5.1%提高至9.8%。该策略是人工方法改进自然光合作用的一个新尝试。
相关研究成果以“Enhancing photosynthetic CO2 fixation by assembling metal-organic frameworks on Chlorella pyrenoidosa”为题,于近日以Editors' Highlights形式发表在《自然—通讯》(Nature Communications)上。该工作的共同第一作者是我组博士研究生李定颐和博士后董鸿。以上工作得到国家自然科学基金委“人工光合成”基础科学中心、国家自然科学基金、中国科学院青促会等项目的资助。(文/图 李定颐、王旺银)
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40839-0