我组利用operando技术揭示CO2加氢制甲醇催化机理
Utilizing renewable energy such as solar energy to produce hydrogen from water splitting through photocatalysis, photocatalysis or electrocatalysis coupled with CO2 hydrogenation to produce methanol and other fuels is an effective strategy to achieve the goal of carbon neutrality, and it is also one of the important paths for artificial photosynthesis. This work uses operando technology and theoretical calculation to track the surface reaction process and catalyst performance at the same time. The results show that the Zn-O-Zr asymmetric active site on the ZnZrOx catalyst is important for the formation and conversion of intermediates,such as carbonate and formate species. In the initial stage of the reaction, CO2 is mainly adsorbed on the surface as bidentate carbonate species, and H2 is activated in the form of heterolytic dissociation. The Hδ- species produced by H2 heterolytic dissociation and Cδ+ center in the species (CO3*, HCOO*, H2CO*, etc.) undergoes a nucleophilic reaction, easily forms C-H bonds which couples an equimolar proton transfer process to produce methanol. During the whole reaction process, the Zn-O-Zr asymmetric sites on the surface of ZnZrOx catalyst showed the synergistic effects at the atomic level (Zn sites promoted the heterolytic dissociation of H2, and Zr sites stabilized the adsorbed carbon-oxygen species), so it was found that such adjacent heterogeneous asymmetric sites are the essential reason for the high-performance synthesis of methanol.
近日,我组在CO2加氢制甲醇的机理研究方面取得新进展。利用operando IR-MS技术,揭示了ZnZrOx固溶体催化剂上相邻的Zn-O-Zr不对称活性中心对于CO2活化和催化加氢的协同促进机理。
利用太阳能等可再生能源,通过光催化、光电催化或电催化分解水制氢耦合CO2加氢制甲醇等燃料或化学品是实现碳中和目标的有效策略,也是人工光合成的重要路径之一。CO2加氢制甲醇过程中,产物的选择性调控和催化剂稳定性是制约甲醇高效制备的关键因素,针对该问题,李灿院士团队前期研发了一系列双金属氧化物固溶体催化剂(Sci Adv. 2017; ACS Catal. 2019),以ZnZrOx催化剂为代表,该类催化剂可以同时实现甲醇合成的高选择性和稳定性。此外,对ZnZrOx固溶体催化剂的改性和掺杂可进一步提高反应的催化性能(J Catal. 2021; J Catal. 2021; Chinese Journal of Catalysis. 2023)。目前,固溶体催化剂已被国内外研究者广泛应用于二氧化碳转化制甲醇及其他二氧化碳加氢转化反应。尽管如此,H2和CO2在固溶体催化剂表面的吸附活化及吸附物种如何加氢转化为甲醇的微观机理等仍不甚清楚。
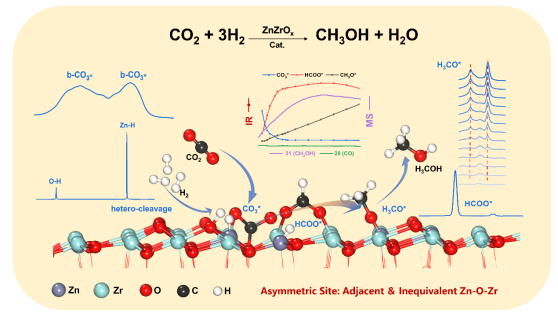
本工作利用operando技术和理论计算方法,同时对表面反应过程和催化剂性能进行跟踪,结果表明,ZnZrOx催化剂上Zn-O-Zr不对称活性中心对于碳酸盐和甲酸盐中间物种的形成和转化都起到了活化和促进作用,反应起始阶段,CO2主要以双齿构型的碳酸盐物种在表面吸附,H2则以异裂解离的形式活化,H2异裂解离产生的Hδ-物种和碳氧物种(CO3*,HCOO*,H2CO*等)中的Cδ+中心发生亲核反应,容易形成C-H键,耦合等摩尔量的质子转移过程产生甲醇。在整个反应过程中,催化剂表面的Zn-O-Zr不对称位点表现出了原子水平的协同作用(Zn位点促进H2的异裂解离,Zr位点稳定吸附的碳氧物种),因此发现这类相邻异质的不对称活性中心是催化甲醇高性能合成的本质原因。
相关研究成果以“Asymmetric sites on ZnZrOx catalyst for promoting formate formation and transformation in CO2 hydrogenation.”为题,于近日以全文形式发表在《美国化学会志》(Journal of the American Chemical Society)上。该工作的第一作者是我所博士研究生冯振东。上述工作得到了国家自然科学基金委,“人工光合成”基础科学中心项目(FReCAP, 22088102)的支持。(文/图 冯振东)
文章链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/jacs.3c02248
链接地址:
Sci Adv.2017: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.1701290
ACS Catal.2019: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acscatal.9b03449
J Catal.2021: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021951721000853
J Catal.2021: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021951721004024?via%3Dihub
Chinese Journal of Catalysis. 2023: https://www.cjcatal.com/EN/10.1016/S1872-2067(22)64176-7