Insights into How NH4+ Ions Enhance the Activity of Dimeric G-Quadruplex/Hemin DNAzyme
Wenqin Zhou, Rui Lai, Yu Cheng, Yu Bao, Wenhui Miao, Xupeng Cao, Guoqing Jia*, Guohui Li*, and Can Li*
ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 7, 4330–4338
Dimeric G-quadruplex (G4)/Hemin has been employed to expand the catalytic repertoire of nucleic acid. Herein, we aim to understand the effect of NH4+ ions on the catalytic behavior of the dimeric G4/Hemin DNAzyme. Through EPR and UV–vis spectroscopy, we found that NH4+ ions resulted in more accumulation of compound I (Cpd I, Fe (IV)═O•+) in the dimeric DNAzyme process. Furthermore, molecular dynamics simulations showed that NH4+ ions could be present in the catalytic chamber to stabilize the dimeric G4 while interacting with the substrate hydrogen peroxide by hydrogen bonds. The interaction between the NH4+ ion and H2O2 contributes to a better stability of intermediate and transition-state species involved in the catalytic formation of Cpd I. Specifically, NH4+ ions facilitate the O–O bond breaking of iron–porphyrin-bound H2O2 (the rate-limiting step). With four available hydrogen atoms, a NH4+ ion can be an effective “additive” to promote the activity of the dimeric DNAzyme. The results provide the strategy for adjusting the DNAzyme by transition-state stabilization by hydrogen bonding networks. Our data shed light on the mechanistic clues on the design and application of G4-based catalysts.
近日,我组在四链体核酸(G4-DNA)催化机理研究方面取得新进展,研究发现铵根离子的加入可显著提升DNAzyme的催化活性,通过优化调变系列铵盐对活性的影响,证明了在催化活性中心氢键网络的形成对稳定过渡态中间体具有重要作用。
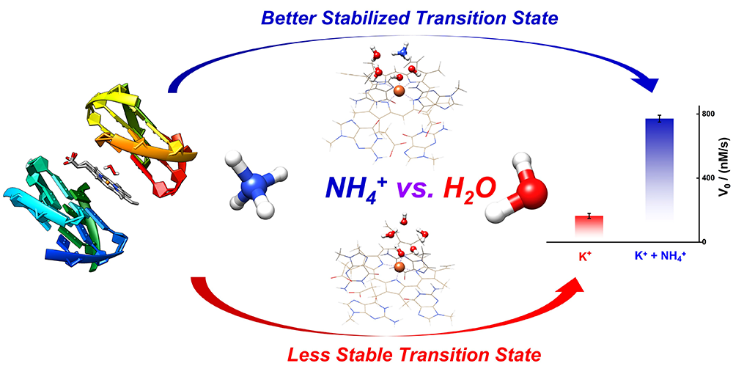
G4/Hemin体系极大的扩展了DNAzyme的催化库,已被广泛应用于核酸催化剂和生物传感器,更值得关注的是近年来的研究发现该体系在生物细胞中真实存在。在本工作中,实验发现了铵根对DNAzmye 的活性可显著提高。通过EPR和UV-vis光谱分析表明,NH4+的添加将导致化合物I (Cpd I, Fe (IV)=O·+)的大量积累。此外,分子动力学模拟表明,NH4+可以在催化中心稳定二聚体G4,同时与底物过氧化氢通过氢键相互作用。与水分子相比,NH4+和H2O2之间的相互作用有助于提高过渡态物种的稳定性。该工作对设计高效的DNAzyme提供了催化机理线索,也促进了生物催化剂的潜在应用。
我组长期致力于探索DNA相关的催化功能,旨在将这种化学功能与生命过程相关联,进而发展从源头上为防止和治疗疾病的策略与技术。近年来取得了系列成果,特别是在DNA酶催化反应类型方面,前期发现了人端粒G4-DNA能够催化不对称Diels-Alder反应(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2012)(Chem. Sci.2015),Friedel-Crafts(Chem. Commun.2015)反应以及不对称环丙烷化反应(ACS.Catal., 2020)(Chem. Sci.2021),同时报道了高活性的自组装二聚DNAzyme(Chem. Sci.2020)(Anal. Chem. 2021)。 此外,在G4-DNA结构功能研究方面发现loop区序列的排列组合方式(Nucleic Acids Res.2018)以及配体的作用模式(Biochemstry. 2021)对G4-DNA的二级结构的稳定性具有重要影响。以上工作对认识与理解DNA化学功能与生物过程的关联提供了新思路。
相关研究成果以“Insights into How NH4+ Ions Enhance the Activity of Dimeric G-quadruplex/Hemin DNAzyme”为题,发表在ACS Catalysis上。该工作的理论模拟部分由化学动力学研究室李国辉研究员团队的赖睿博士完成。上述工作得到国家重点研发计划、国家自然科学基金委项目的资助。(文/图 周文琴)
文章链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acscatal.2c05905