Linking the Photoinduced Surface Potential Difference to Interfacial Charge Transfer in Photoelectrocatalytic Water Oxidation
Ruotian Chen, Deyun Zhang, Ziyuan Wang, Dongfeng Li, Lingcong Zhang, Xiuli Wang, Fengtao Fan*, and Can Li*
J. Am. Chem. Soc.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.2c12704
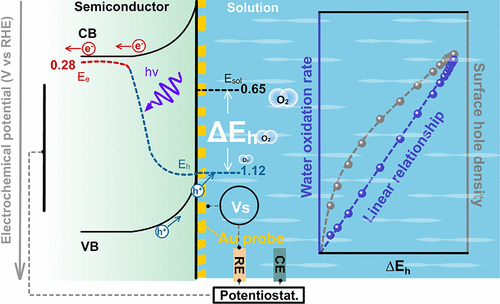
Charge transfer at the semiconductor/solution interface is fundamental to photoelectrocatalytic water splitting. Although insights into charge transfer in the electrocatalytic process can be gained from the phenomenological Butler–Volmer theory, there is limited understanding of interfacial charge transfer in the photoelectrocatalytic process, which involves intricate effects of light, bias, and catalysis. Here, using operando surface potential measurements, we decouple the charge transfer and surface reaction processes and find that the surface reaction enhances the photovoltage via a reaction-related photoinduced charge transfer regime as demonstrated on a SrTiO3 photoanode. We show that the reaction-related charge transfer induces a change in the surface potential that is linearly correlated to the interfacial charge transfer rate of water oxidation. The linear behavior is independent of the applied bias and light intensity and reveals a general rule for interfacial transfer of photogenerated minority carriers. We anticipate the linear rule to be a phenomenological theory for describing interfacial charge transfer in photoelectrocatalysis.
近日,我组在太阳能光催化半导体溶液界面电荷转移机制研究中取得新进展。通过结合纳米金属电极、原位光电化学和差分放大的办法,创新地发展了原位在线条件下光(电)催化体系表界面电化学势和光电压的微观测量技术,揭示了光电催化水氧化过程中的光诱导的表面电势差与水氧化速率之间的普适性线性规律,明晰了光驱动的半导体溶液界面电荷转移的本质驱动力,建立了对光催化界面电荷转移理论的新的认识。
太阳能光催化反应是一个涉及多电子转移的能量爬坡过程,光生电荷分离后发生电荷的转移、复合,最终参与表面催化反应,整个过程跨越巨大的时间和空间尺度,这使得理解和认识该过程的复杂机制十分困难。针对此过程,我组发展了高分辨表面光电压成像新方法(Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018),实现光生电荷的可视化研究,围绕光催化高效电荷分离研究取得了一系列进展(Nano Lett., 2017; Nature Energy, 2018; Nano Lett., 2019; Adv. Matter., 2020; Angew, 2022),近期又发展了全时空动态成像原创方法(Nature, 2022),揭示光催化剂中复杂的多重电荷转移新机制。这些工作深入揭示了光生电荷从光催化剂内部向表面分离和转移的微观机制。
在上述的理解和认识的基础上,在液相反应条件下研究光生电荷跨越固液相界面向化学能转化的过程成为理解整个太阳能光化学转换过程的“最后一公里”。本工作聚焦于理解光催化剂表面光生电荷如何通过半导体溶液界面转移驱动水分解反应这一核心科学问题,在钛酸锶光催化剂水氧化反应过程中,利用自主研发的operando表界面电化学势测量方法,同时对光催化剂表面和溶液电化学势、电子和空穴的准费米能级、体系光电压和表面水氧化活性进行检测,成功解耦了光电催化水分解过程中错综复杂的电荷转移步骤与催化反应步骤,发现了全新的表面催化反应促进的电荷转移机制。通过定量关联揭示了这种全新的电荷转移机制引起的光催化剂表面与溶液之间的电势差是界面电荷转移的本质驱动力,且这种驱动力与界面电荷转移速率具有线性规律。进一步深入研究发现这种线性规律对光生少子界面电荷转移和利用具有普适性,区别于Bulter-Volmer理论描述的电催化过程电压与界面电荷转移速率之间的指数规律。其内在原因是在光电催化过程中光照和外加偏压只是改变参与反应的电荷浓度,不改变参与反应的表面电荷的能量和反应坐标。这些结果建立了对光催化界面电荷转移理论的全新认识。
相关研究成果以“Linking photoinduced surface potential difference to interfacial charge transfer in photoelectrocatalytic water oxidation”为题,于近日发表在《美国化学会志》(Journal of the American Chemical Society)上。该工作的第一作者是我组陈若天副研究员和博士研究生张德云与王子芫,通讯作者是李灿院士和范峰滔研究员,上述工作得到了国家科技部国家重点研发计划、国家自然科学基金委“人工光合成”基础科学中心、中国科学院稳定支持基础研究领域青年团队计划、我所创新基金等项目的支持。(文/图 陈若天 张德云)
文章链接: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.2c12704
文章相关文献链接:
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018:
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CS00320C
Nano Lett., 2017:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b02799
Nature Energy, 2018:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41560-018-0194-0
Nano Lett., 2019:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04245
Adv. Matter., 2020:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201906513
Angew, 2022:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202117567
Nature, 2022:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05183-1